Memo List July
反正经常开坑不填,为了保持版面整洁,先在Memo里开坑,待填的差不多了再单独拿出去。
[2017-07-30 17:46:32]
Linux内核分析与实现
ULK 2014
hw1
- 阅读至少2本操作系统相关书籍,
- 给出这些书中关于操作系统的定义,要列出出处。
- 阐明操作系统的公共设计目标和某些操作系统特有的设计目标,要列出出处。
- 阐明操作系统的作用,要列出出处。
- 根据你对操作系统的理解, 画出操作系统的层次模块图(自由发挥,合乎逻辑)。
- 操作系统的基本类型是哪三种?它们的关键技术有哪些?
- 使用一张表,简要列出操作系统发展各个阶段的年代、器件技术、操作系统突破的关键技术问题。
- 多道程序设计的主要优点是什么?多道程序对操作系统的功能需求有哪些?
[2017-07-29 16:48:13]
Arch 里面换了systemd-netwoekd 配置网络,一直不成功。想看一下log 结果journal坏掉了,如下
➜ ~ systemctl status systemd-journald.service
● systemd-journald.service - Journal Service
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/systemd-journald.service; static;
Active: failed (Result: exit-code) since Sat 2017-07-29 16:58:02 CST; 52s
Docs: man:systemd-journald.service(8)
man:journald.conf(5)
Process: 184 ExecStart=/usr/lib/systemd/systemd-journald (code=exited, stat
Main PID: 184 (code=exited, status=1/FAILURE)
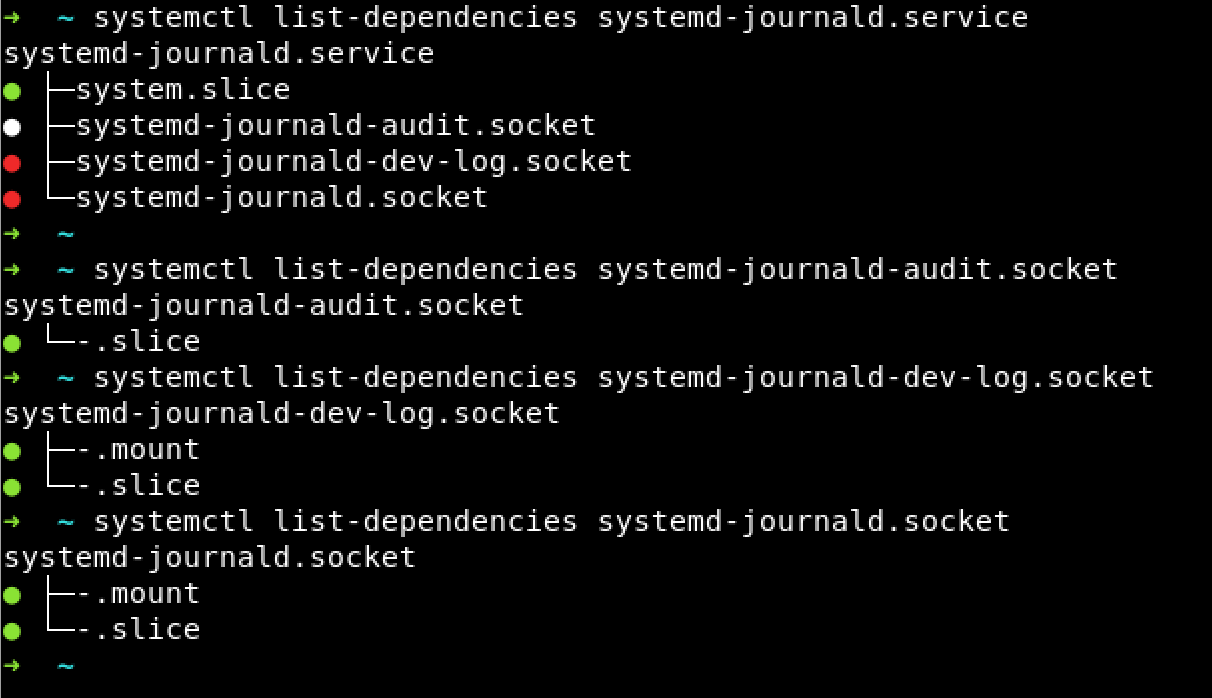
systemctl list-dependencies systemd-journald.service
查看启动依赖
发现有几个依赖项没有启动,手工拉一下
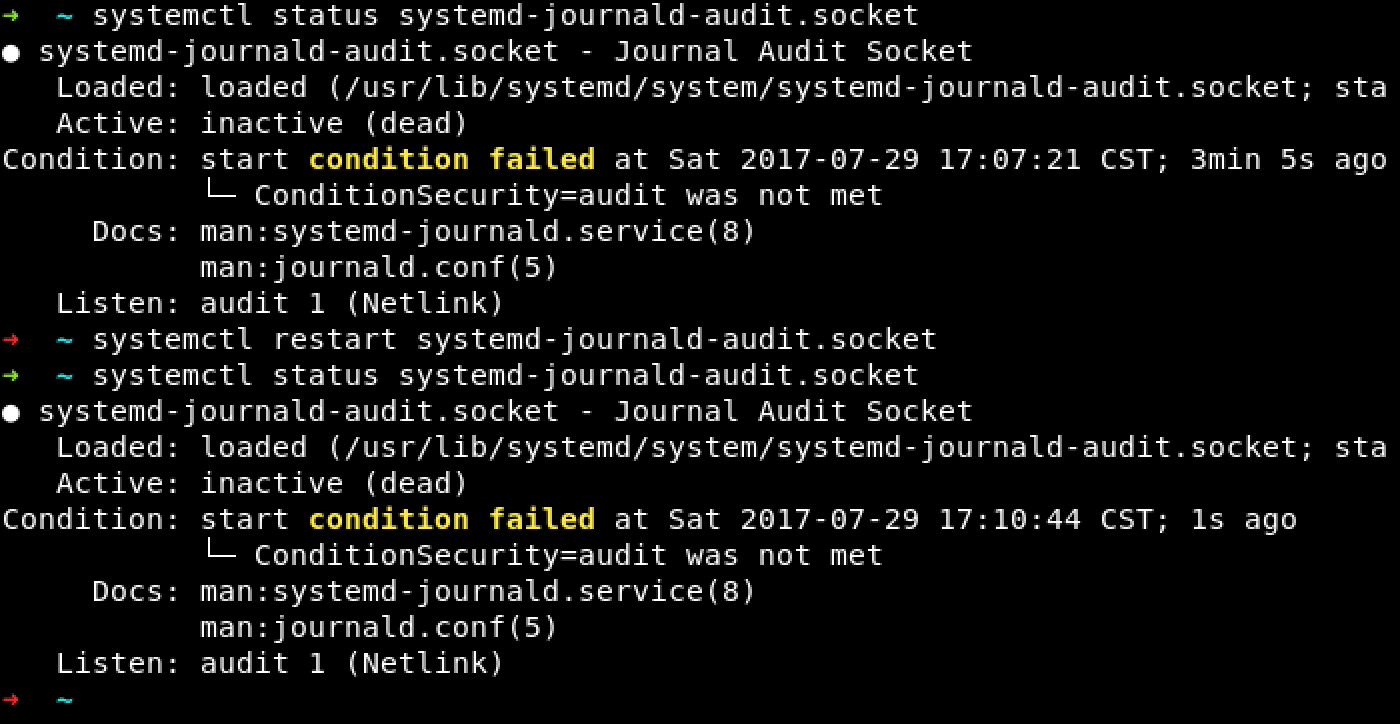
开了下其中一个的状态,并尝试重启了下. 无效
systemctl --all --failed
ref;
-
[SOLVED] journald not logging / System Administration / Arch Linux Forums 然而并没有出现这个问题
-
Arch Linux ARM • View topic - Issuses with 1Aug2016 "latest" for utilite 这个要重装内核...
Got it working by updating uboot and switching to the >linux-image-imx6 kernel, resetting and updating the uboot env >with the help of these threads:
....
pacman -Syu installed the new glibc and it didn't blow up! Hooray. Now to rebuild all my configurations.
@DevilCrayon
-
Bug 1379800 – systemd does not create new machine-id file if none is present 以上两个bug 互相关联
附 dmesg-log dmesg-err.txt
cis 914
01-intro Haskell 入门
推荐阅读: 【en】
- Starting Out - Learn You a Haskell for Great Good!, chapter 2
- Real World Haskell, chapters 1 and 2
【zh-cn】
什么是 Haskell
Haskell 的特点:
- 函数式[语言/编程] (Functional)
- 纯函数 (Pure)
- 惰性求值 (Lazy)
- 静态类型 (Statically typed)
Themes
三个关注的方面
- 类型 (Types)
- 抽象 (Abstraction)
- Wholemeal programming
[2017-07-15 22:02:13]
Some Note for FreeCodeCamp
当你遇到困惑不知道该怎么办,永远记住:Read-Search-Ask。
- Read the error
- Search Google
- Ask for help
HTML 5 & CSS
Say Hello to HTML Element
HTML(Hyper Text Markup Language)(超文本标记语言)
大部分元素都有一个开始标记和一个结束标记。
h1就是一个HTML元素,h1是header1的简写,意思是 一级标题。
h1是主标题,h2是副标题,h3、h4、h5、h6依次递减字体的大小。
p是英文paragraph段落的缩写,经常被用来创建一个段落.
注释有两个功能:
- 想让某一段代码不起作用,但你又不想删除这一段代码。
- 就是给代码添加一些说明,方便团队合作或日后自己查看,但又不想影响代码本身。
注释的开始标记是<!--
结束
Change the Color of Text
我们可以通过修改元素的style(样式)来达到目的。 样式的属性有很多,其中color用来指定颜色。
以下是将你的h2元素的文本颜色设置为蓝色的示例代码:
<h2 style="color: blue">CatPhotoApp</h2>
Use CSS Selectors to Style Elements
样式的属性多达几千个,但别担心,按照80-20原则,常用的也就几十个,你完全可以掌握它。
当你键入 <h2 style="color: red">CatPhotoApp</h2>,你就给h2元素添加了inline style(内联样式)。
内联样式是为元素添加样式的最简单有效的方式,但是更易于维护的方式是使用层叠样式表CSS(Cascading Style Sheets)。
在代码的最顶端,创建一个如下的style元素:
<style>
</style>
在这个style元素内, 你可以为所有的h2元素创建一个元素选择器。比如,如果你想要将所有的h2元素设置为红色, 你的代码应该看起来像这样:
<style>
选择器 {属性名称: 属性值;}
h2 {color: red;}
</style>
注意:一定要在属性值的后面加上分号;。
Use a CSS Class to Style an Element
- 我们先声明一个类选择器:
<style>
.blue-text {
color: blue;
}
</style>
上面的代码在 <style> 标记中声明了一个叫做 blue-text 的类样式。
- 然后在h2元素上应用我们声明的类选择器:
<h2 class="blue-text">CatPhotoApp</h2>
注意:在CSS中,类选择器应该添加.为前缀。
而在HTML中,class属性不能添加.为前缀。 这是因为在CSS中如果类选择器前不添加. 浏览器就会误认为类选择器是一个元素选择器。
Change the Font Size & Font Family of an Element
字号是由样式属性font-size来控制的, 如下:
h1 {
font-size: 30px;
}
用font-family属性来设置元素的字体。
如果你想把副标题的字体设置为Sans-serif,你可以使用下面的CSS:
h2 {
font-family: Sans-serif;
}
Import a Google Font
现在,让我们来导入谷歌字体。
首先,你需要用link标签来引入谷歌Lobster字体。
复制下面的代码片断并将其粘贴到你的代码编辑器的顶部:
<link href="https://fonts.gdgdocs.org/css?family=Lobster" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
现在你可以将Lobster作为 font-family属性 的值应用到你的h2元素上了。
Specify How Fonts Should Degrade
有几种默认的字体是所有浏览器都可用的,包括Monospace、Serif和Sans-Serif。
当某种字体不可用时,你可以让浏览器自动降级到另一种字体。
例如,如果你想让段落的字体为Helvetica,但你同时想在Helvetica字体不可用时自动降级使用Sans-Serif字体,你可以使用如下CSS样式:
p {
font-family: Helvetica, Sans-Serif;
}
Add Images to your Website
使用img元素来为你的网站添加图片,使用src属性指向一个图片的具体地址。
举例如下:
<img src="https://www.your-image-source.com/your-image.jpg">
注意:img元素是自关闭元素,不需要结束标记。
Size your Images
CSS包含一个控制元素宽度的width属性。像控制字体一样,我们使用px(像素)来指定图片的宽度。
例如,如果我们想要创建一个名为larger-image的类选择器,把HTML元素的宽度设定为500像素,我们使用:
<style>
.larger-image {
width: 500px;
}
</style>
Add Borders Around your Elements
CSS 边框的属性有style(样式)、color(颜色)、width(宽度)、height(高度)等。
举个例子,如果我们想要让一个HTML元素的边框颜色为红色、边框宽度为5像素(px)、边框样式为固体(solid),代码如下:
<style>
.thin-red-border {
border-color: red;
border-width: 5px;
border-style: solid;
}
</style>
提示:你可以应用多个class到一个元素,只需要在多个class之间用 空格 分开即可。例如:
<img class="class1 class2">
Add Rounded Corners with a Border Radius
猫咪图片的边框现在是尖尖的,不够可爱,我们可以通过CSS的一个叫border-radius(边框半径)的属性来让它的边框变成圆的。
除了像素,你还可以使用百分比来指定border-radius边框半径的值。
Link to External Pages with Anchor Elements
a元素,也叫anchor(锚点)元素,既可以用来链接到外部地址实现页面跳转功能,也可以链接到当前页面的某部分实现内部导航功能。
↓ ancher tag ↓ anchor tag's href attribute
<p>Here's a <a href="http://freecodecamp.cn"> link to FreeCodeCamp中文社区 </a> for you to follow.</p>
↑ link's text
Nesting(嵌套)就是把一个元素放在另一个元素里面。
Make Dead Links using the Hash Symbol
有时你想为你的网站添加一个a元素,但此时你还不知道要将它们链接到哪儿,此时可以使用固定链接。
把你的a元素的href属性的值替换为一个#,别名hash(哈希)符号,将其变为一个固定链接。
Turn an Image into a Link
你可以通过把某元素嵌套进a元素使其变成一个链接。
把你的图片嵌套进a元素。举例如下:
<a href="#"><img src="/images/relaxing-cat.jpg"></a>
Add Alt Text to an Image for Accessibility
alt属性,也被称为alt text, 是当图片无法加载时显示的替代文本。alt属性对于盲人或视觉损伤的用户理解一幅图片中所描绘的内容非常重要,搜索引擎也会搜索alt属性。
简而言之,每一张图片都应该有一个alt属性!
你可以像下面例子中一样为img元素添加一个alt属性:
<img src="www.your-image-source.com/your-image.jpg" alt="your alt text">
List
Create a Bulleted Unordered List
HTML有一个特殊元素,用于创建unordered lists(无序列表), 或带项目符号的列表。
无序列表以 <ul> 元素开始,并包含一个或多个 <li> 元素。
例如:
<ul>
<li>milk</li>
<li>cheese</li>
</ul>
将会创建一个带项目符号的"milk"和"cheese"列表。
Create an Ordered List
HTML有一个特殊元素,用于创建ordered lists(有序列表), 或数字编号列表。
有序列表以<ol>元素开始,并包含一个或多个<li>元素。
例如:
<ol>
<li>Garfield</li>
<li>Sylvester</li>
</ol>
将创建一个包含"Garfield"和"Sylvester"的数字编号列表。
Form, Button and Checkboxes
Create a Text Field
现在让我们来创建一个form(表单)。
Text input(文本输入框)是用来获得用户输入的绝佳方式。
你可以用如下方法创建:
<input type="text">
注意,input元素是自关闭的。
Add Placeholder Text to a Text Field
占位符(placeholder text)是用户在input(输入)框输入任何东西之前放置在input(输入)框中的预定义文本。
你可以用如下方式创建占位符:
<input type="text" placeholder="this is placeholder text">
Create a Form Element
使用HTML来构建可以跟服务器交互的Web表单(form),通过给你的form元素添加一个action属性来达到此目的。
action属性的值指定了表单提交到服务器的地址。
例如:
<form action="/url-where-you-want-to-submit-form-data"></form>
Add a Submit Button to a Form
让我们来为你的form添加一个submit(提交)按钮,点击这个按钮,表单中的数据将会被发送到你通过action属性指定的地址上。
下面是submit按钮的例子:
<button type="submit">this button submits the form</button>
Use HTML5 to Require a Field
当你设计表单时,你可以指定某些选项为必填项(required),只有当用户填写了该选项后,用户才能够提交表单。
例如,如果你想把一个文本输入字段设置为必填项,在你的input元素中加上required属性就可以了,你可以使用:
<input type="text" required>
注意:required属性在Safari浏览器中不起作用,请用其他浏览器来学习,推荐使用Chrome。
Create a Set of Radio Buttons
单选就是你只能在多个选项中选择一个,就好比你有很多追求者,但却只能选择一个结婚。
多选一的场景就用radio button(单选按钮)
单选按钮只是input输入框的一种类型。
每一个单选按钮都应该嵌套在它自己的label(标签)元素中。
注意:所有关联的单选按钮应该使用相同的name属性。
下面是一个单选按钮的例子:
<label><input type="radio" name="indoor-outdoor"> Indoor</label>
<label><input type="radio" name="indoor-outdoor"> Outdoor</label>
Create a Set of Checkboxes
当你在大学选课时,面对几百门课程,而因为时间和精力,你只能从中选择十几门。
这样的场景就用checkboxes(复选按钮)。
复选按钮是input的输入框的另一种类型。
每一个复选按钮都应该嵌套进label元素中。
所有关联的复选按钮应该具有相同的name属性。
下面是复选按钮的例子:
<label><input type="checkbox" name="personality"> Loving</label>
<label><input type="checkbox" name="personality"> Loving2</label>
<label><input type="checkbox" name="personality"> Loving3</label>
Check Radio Buttons and Checkboxes by Default
使用checked属性,你可以设置复选按钮和单选按钮默认被选中。
为此,只需在input元素中添加属性checked
<input type="radio" name="test-name" checked>
<label><input type="checkbox" name="personality" checked> Loving</label>
Div
Nest Many Elements within a Single Div Element
div元素,也被称作division(层)元素,是一个盛装其他元素的通用容器。
所以可以利用CSS的继承关系把div上的CSS传递给它所有子元素。
你可以用<div>来标记一个div元素的开始,然后用</div>来标记一个div元素的结束。
Give a Background Color to a Div Element
你可以用 background-color 属性来设置一个元素的背景颜色。
例如,如果你想把一个元素的背景颜色设置为green,你应该把这些加到你的 style 元素中:
.green-background {
background-color: green;
}
Set the ID of an Element
除了 class属性之外,每一个 HTML 元素还可以使用 id 属性。
使用 id 属性有若干好处,一旦当你开始使用 jQuery 的时候你会有更深的体会。
id 属性应该是唯一的,虽然浏览器并不强制唯一,但基于最佳实践,这一点是被广泛认可的,所以请不要给一个以上的元素设置相同的 id 属性。
下面举例说明了如何设置h2 元素的id属性为cat-photo-app
<h2 id="cat-photo-app">
Use an ID Attribute to Style an Element
和类选择器一样,你也可以使用ID选择器来声明样式。
声明一个叫cat-photo-element的ID选择器 ,并设置背景色为绿色。:
##cat-photo-element {
background-color: green;
}
注意:在你的 style 元素内部,定义类选择器必须添加 . 为前缀,定义ID选择器必须添加 # 为前缀。
padding, margin and border
Adjusting the Padding of an Element
你可能早已经注意到了这点,所有的 HTML 元素本质上是小的矩形块,代表着某一小块区域。有三个影响HTML元素布局的重要属性:padding(内边距)、margin(外边距)、border(边框)。
元素的 padding 控制 元素内容/content和 元素边框/border 之间的距离。
Add Different Padding to Each Side of an Element
有时你想要自定义元素,使它的每一个边具有不同的 padding。
CSS 允许你使用 padding-top、padding-right、padding-bottom 和 padding-left来控制元素上右下左四个方向的 padding。
Use Clockwise Notation to Specify the Padding of an Element
除了分别指定元素的属性外,你还可以集中起来指定它们,举例如下:
padding: 10px 20px 10px 20px;
这四个值以顺时针方式排列:顶部、右侧、底部、左侧,简称:上右下左。
Adjusting the Margin of an Element
元素的 外边距/margin 控制 元素边框/border 和元素实际所占空间的距离。
Add a Negative Margin to an Element
如果你将一个元素的 margin 设置为负值,元素将会变大。
Add Different Margins to Each Side of an Element
有时你想要自定义元素,使它的每一个边具有不同的 margin。
CSS 允许你使用 margin-top、margin-right、margin-bottom 和 margin-left 来控制元素上右下左四个方向的 margin。
Use Clockwise Notation to Specify the Margin of an Element
除了分别指定元素的属性外,你还可以集中起来指定它们,举例如下:
margin: 10px 20px 10px 20px;
这四个值以顺时针方式排列:顶部、右侧、底部、左侧,简称:上右下左。
css
Style the HTML Body Element
现在让我们来一个全新的开始,讲一讲 CSS 继承。
每一个 HTML 页面都有一个 body 元素。
通过将其 background-color 设置为黑色,我们可以证明 body 元素的存在。
我们可以通过将下面的代码添加到我们的 style 元素来做到这一点:
body {
background-color: black;
}
算法
二分搜索 Binary Search 分治 Divide Conquer 宽度优先搜索 Breadth First Search 深度优先搜索 Depth First Search 回溯法 Backtracking 双指针 Two Pointers 动态规划 Dynamic Programming 扫描线 Scan-line algorithm 快排 Quick Sort
数据结构
栈 Stack
队列 Queue
链表 Linked List
数组 Array
哈希表 Hash Table
二叉树 Binary Tree
堆 Heap
并查集 Union Find
字典树 Trie
[2017-07-09 15:00:07]
Learn you a Haskell for Great good
中文版
01 introduction
- Haskell 是一门 纯粹函数式编程语言 (purely functional programming language) 无 副作用 (side effect)
- Haskell 是 惰性 (lazy) 的
- Haskell 是 静态类型 (statically typed) 的 支持 自动类型推导 (tyoe inference)
WinGHCi
在GHCi中在载入(:load/:l)文件后,若更改了源文件要记得重新加载源文件(:reload/:r)
02 starting out
Ready, set, go!
GHCi的提示符默认是Preload可以通过:set prompt "ghci>"修改成你想要的形式
简单的运算
ghci> 1+1
2
ghci> 1/3
0.3333333333333333
ghci> div 3 1
3
ghci> div 9 5
1
ghci> 9 `div` 5
1
/默认结果为小数,div为整除
可以通过加上反引号(`),将函数写在中间
负数
ghci> -1
-1
ghci> -1 *9
-9
ghci> 9* -1
<interactive>:15:1: error:
Precedence parsing error
cannot mix ‘*’ [infixl 7] and prefix `-' [infixl 6] in the same infix expression
ghci> 9*(-1)
-9
haskell 里面的-为一个函数。所以负数一般都要加上括号(句首可以不用加)
逻辑运算
ghci> True || False
True
ghci> True && False
False
ghci> not True
False
ghci> ^ True
<interactive>:22:1: error: parse error on input ‘^’
ghci> True | False
<interactive>:23:14: error:
parse error (possibly incorrect indentation or mismatched brackets)
ghci> True and False
<interactive>:24:1: error:
? Couldn't match expected type ‘([Bool] -> Bool) -> Bool -> t’
with actual type ‘Bool’
? The function ‘True’ is applied to two arguments,
but its type ‘Bool’ has none
In the expression: True and False
In an equation for ‘it’: it = True and False
? Relevant bindings include it :: t (bound at <interactive>:24:1)
- 与
|| - 或
&& - 非
not
比较运算符
ghci> 1 == 2
False
ghci> 1 ?= 9
<interactive>:26:3: error:
? Variable not in scope: (?=) :: Integer -> Integer -> t
? Perhaps you meant one of these:
‘>=’ (imported from Prelude), ‘==’ (imported from Prelude),
‘/=’ (imported from Prelude)
ghci> 1 >= 9
False
ghci> 1 /= 9
True
ghci> True == False
False
ghci> "a" == 'a'
<interactive>:30:8: error:
? Couldn't match expected type ‘[Char]’ with actual type ‘Char’
? In the second argument of ‘(==)’, namely ‘'a'’
In the expression: "a" == 'a'
In an equation for ‘it’: it = "a" == 'a'
ghci> 'a' == 'a'
True
ghci> 1 === 2
<interactive>:32:3: error:
? Variable not in scope: (===) :: Integer -> Integer -> t
? Perhaps you meant ‘==’ (imported from Prelude)
ghci> 1 == True
<interactive>:33:1: error:
? No instance for (Num Bool) arising from the literal ‘1’
? In the first argument of ‘(==)’, namely ‘1’
In the expression: 1 == True
In an equation for ‘it’: it = 1 == True
- 大于?
>= - 小于?
<= - 等于?
== - 不等?
/=
不同类型之间不能判定是否相等,Bool值和0/1没有关系
函数
ghci> succ 9 + max 5 4 + 1
16
ghci> (succ 9) + (max 5 4) + 1
16
ghci> succ 9 * 10
100
ghci> succ (9 * 10)
91
函数的优先级最高(>9)
haskell 中的函数调用不需要括号
Baby's first functions
此节至本章末尾的函数定义:
ref: 02-starting out.lhs
- haskell 中的函数定义没有顺序
- haskell 中
if语句的else不可省略 - 函数名中的单引号
'没有特殊含义,只是用来区分不同的函数 - 首字母大写的函数是不允许的
- 常量(函数)不可修改
An intro to lists
** lists, strings and list comprehensions**
Note: 在 ghci 下,我们可以使用
let关键字来定义一个常量。在 ghci 下运行let a=1与在脚本中编写a=1是等价的。
ghci> let lostNumbers = [4,8,15,16,23,48]
ghci> lostNumbers
[4,8,15,16,23,48]
ghci> [4,8,15,16,23,48]
[4,8,15,16,23,48]
ghci> [1,2,'a',3,'b','c',4]
<interactive>:39:2: error:
? No instance for (Num Char) arising from the literal ‘1’
? In the expression: 1
In the expression: [1, 2, 'a', 3, ....]
In an equation for ‘it’: it = [1, 2, 'a', ....]
ghci> ['h','e','l','l','o']
"hello"
- List里面元素的类型必须相同
- 字符串是字符list的语法糖
++
++是用来连接list的操作符
ghci> "hello" ++ " " ++ "world"
"hello world"
ghci> [1,2,3,4] ++ [9,10,11,12]
[1,2,3,4,9,10,11,12]
ghci> ['w','o'] ++ ['o','t']
"woot"
ghci> ['w','o'] ++ "class"
"woclass"
++在插入元素时会遍历整个list,效率很低- 使用
:在lsit前面添加元素效率更高
:
:用来在list头部插入 一个 元素
ghci> '!' : ['w','o']
"!wo"
ghci> "hi" : ['w','o']
<interactive>:48:9: error:
? Couldn't match expected type ‘[Char]’ with actual type ‘Char’
? In the expression: 'w'
In the second argument of ‘(:)’, namely ‘['w', 'o']’
In the expression: "hi" : ['w', 'o']
<interactive>:48:13: error:
? Couldn't match expected type ‘[Char]’ with actual type ‘Char’
? In the expression: 'o'
In the second argument of ‘(:)’, namely ‘['w', 'o']’
In the expression: "hi" : ['w', 'o']
ghci> 'A':" SMALL CAT"
"A SMALL CAT"
ghci> 5:[1,2,3,4,5]
[5,1,2,3,4,5]
Note:
[],[[]],[[],[],[]]是不同的。第一个是一个空的 List,第二个是含有一个空 List 的 List,第三个是含有三个空 List 的 List。
ghci> []
[]
ghci> [[]]
[[]]
ghci> [] == [[]]
False
ghci> [] : [[]]
[[],[]]
ghci> [] : [] : []
[[],[]]
ghci> ([] : []) : []
[[[]]]
!!
!!用于按照顺序从list 里面取值,索引从0开始
ghci> "Steve Buscemi" !! 0
'S'
ghci> "Steve Buscemi" !! 3
'v'
ghci> [9.4,33.2,96.2,11.2,23.25] !! 1
33.2
ghci> [9.4,33.2,96.2,11.2,23.25] !! 11
*** Exception: Prelude.!!: index too large
ghci> [9.4,33.2,96.2,11.2,23.25] !! (-1)
*** Exception: Prelude.!!: negative index
索引超出范围会报错
List of list
list可以装入list从而得到多维数组
ghci> let b = [[1,2,3,4],[5,3,3,3],[1,2,2,3,4],[1,2,3]]
ghci> b
[[1,2,3,4],[5,3,3,3],[1,2,2,3,4],[1,2,3]]
ghci> b ++ [[1,1,1,1]]
[[1,2,3,4],[5,3,3,3],[1,2,2,3,4],[1,2,3],[1,1,1,1]]
ghci> it !! 2
[1,2,2,3,4]
ghci> [6,6,6]:b
[[6,6,6],[1,2,3,4],[5,3,3,3],[1,2,2,3,4],[1,2,3]]
ghci> b !! 3
[1,2,3]
it代指上一次的运算结果(仅ghci中有效)
List 中的 List 可以是不同长度,但必须得是相同的类型。
ghci> ["adsf","123"]
["adsf","123"]
ghci> [["adsf"],["123"]]
[["adsf"],["123"]]
ghci> [["adsf"],["123"],[213]]
<interactive>:73:20: error:
? No instance for (Num [Char]) arising from the literal ‘213’
? In the expression: 213
In the expression: [213]
In the expression: [["adsf"], ["123"], [213]]
比较list
当 List 内装有可比较的元素时,使用 > 和 >= 可以比较 List 的大小。它会先比较第一个元素,若它们的值相等,则比较下一个,以此类推。
ghci> [3,2,1] > [2,1,0]
True
ghci> ["abcd"] <= ["xyz"]
True
ghci> "abcd" <= ['a']
False
ghci> "ab" == ['a','b']
True
ghci> [['a']] == ['a']
<interactive>:78:13: error:
? Couldn't match expected type ‘[Char]’ with actual type ‘Char’
? In the expression: 'a'
In the second argument of ‘(==)’, namely ‘['a']’
In the expression: [['a']] == ['a']
ghci> ["abcd"] <= ['a']
<interactive>:76:14: error:
? Couldn't match expected type ‘[Char]’ with actual type ‘Char’
? In the expression: 'a'
In the second argument of ‘(<=)’, namely ‘['a']’
In the expression: ["abcd"] <= ['a']
List 常用函数

ghci> head [5,4,3,2,1]
5
ghci> tail [5,4,3,2,1]
[4,3,2,1]
ghci> last [5,4,3,2,1]
1
ghci> init [5,4,3,2,1]
[5,4,3,2]
Texas ranges
I'm a list comprehension
Tuples
[2017-07-08 13:06:01]
测试 haskell 高亮以及 pandoc lhs转md效果
## 写成这样会显示`lhs`中的`>`。 ↓↓↓↓↓
pandoc -f markdown+lhs -t html+lhs -o 1.html '.\10.2-Identity Monad.lhs'
pandoc -f markdown+lhs -t markdown -o 1.md '.\10.2-Identity Monad.lhs'
pandoc -f markdown -t html -o 2.html 1.md
10.2 Identity Monad
为避免与 Prelude及GHC.Base里面预定义的函数冲突,加上以下几行
不自动导入 Prelude
{-# LANGUAGE NoImplicitPrelude #-}
-- 避开冲突
import Prelude hiding ((>>=), Monad, Identity)
10.2.1 最基本的Monad定义
-- typeclass Monad
class Monad m where
return :: a -> m a
(>>=) :: m a -> (a -> m b) -> m b
(>>) :: m a -> m b -> m b
m >> k = m >>= \_-> k
fail :: String -> m a
fail s = error s
要实现Monad类型类,需要实现return函数和(>>=)运算符。
return函数将一个值a映射为Monad a(>>=)运算符将连续的、从左至右的运算串联起来
10.2.2 Monad.Identity
下面定义一个最简单的Monad——Identity Monad(单位元Monad)
-- Identity Monad
newtype Identity a = Identity { runIdentity :: a }
instance Monad Identity where
-- return a = Identity a
return = Identity
(Identity m) >>= k = k m
10.2.3 (|>)
在讨论高阶函数时,为了把参数写在函数名的前面,定义了一个中缀运算符(|>)
-- 中缀运算符
(|>) = flip ($)
目前看高亮效果一般,大概是主题配色的锅;
pandoc转化有点小问题,代码段头会多出一段,需要手工替换
{.sourceCode .literate .haskell}
另外建议使用=代替#标识标题,#会被转义为\#,需要手工替换
[2017-07-05 13:22:19]
暑假借了本书看
1.1.1 机器码
int gi;
void main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
gi = 12;
}
用vs2015 在赋值语句处下断点,反汇编可得 (关闭显示符号名,打开显示字节码)
gi = 12;
001B168E C7 05 44 81 1B 00 0C 00 00 00 mov dword ptr ds:[001B8144h],0Ch
}
观察机器码,猜测可分为三块
C7 05 | 44 81 1B 00 | 0C 00 00 00
mov | 0x001B8144 | 0x0000000C (12)
说明整数在计算机中按逆序储存。更改gi的值可进一步确认
gi = 0x12345678;
013C168E C7 05 44 81 3C 01 78 56 34 12 mov dword ptr ds:[013C8144h],12345678h
}
C7 05 | 44 81 3C 01 | 78 56 34 12
mov | 013C8144h | 12345678h
大端序:按书写顺序存放。 PowerPC, SUN' SPARC 等为大端序
小端序:整数逻辑上的最低字节放在内存的最低地址,依次存放。 Intel x86 CPU 是小端序
[2017-07-02 09:54:43]
- Atom Haskell Tools
安装atom上的haskell套件时出错了
参照教程
以前也没安装成功,这次先装依赖stack install ghc-mod
Failed to install old-time-1.1.0.3
Build log ( C:\Users\inkyd\AppData\Roaming\stack\logs\old-time-1.1.0.3.log ):
Configuring old-time-1.1.0.3...
configure: WARNING: unrecognized options: --with-compiler
checking for gcc... F:\env\HASKEL~1\8080A1~1.2-A\mingw\bin\gcc.exe
checking whether the C compiler works... no
configure: error: in `/cygdrive/c/Users/inkyd/AppData/Local/Temp/stack-tmp-6820/old-time-1.1.0.3':
configure: error: C compiler cannot create executables
See `config.log' for more details
stack: Leaving directory 'C:\Users\inkyd\AppData\Local\Temp\stack-tmp-6820\old-time-1.1.0.3'
···
stack: Error: some packages failed to install:
cpphs-1.20.8 depends on old-time-1.1.0.3 which failed to install.
ghc-mod-5.8.0.0 depends on old-time-1.1.0.3 which failed to install.
haskell-src-exts-1.19.1 depends on old-time-1.1.0.3 which failed to install.
hlint-2.0.9 depends on old-time-1.1.0.3 which failed to install.
old-time-1.1.0.3 failed during the configure step. The exception was:
ExitFailure 77
找到一个issue
放弃
[2017-06-29 22:52:43]
